Comprehensive Comparison: NMC vs. LFP vs. LTO Batteries – Energy Density, Lifespan, Safety, and Cost
With the rapid advancement of renewable energy technologies, lithium batteries have emerged as the cornerstone for powering electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and various industrial applications. Among the most prominent types are NMC (nickel-manganese-cobalt), LFP (lithium iron phosphate), and LTO (lithium titanate) batteries. Each offers unique performance characteristics, lifespans, safety profiles, and costs, making it essential for businesses, engineers, and consumers to understand their differences.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into a head-to-head comparison across key metrics like energy density, cycle life, charging speed, cost per kWh, safety, environmental impact, and typical uses. This guide aims to help you select the battery that best fits your needs.
What is an NMC Battery? – The High-Energy Density Powerhouse

NMC batteries, or nickel-manganese-cobalt lithium batteries, are widely used in electric vehicles due to their impressive energy density and strong power output.
- Energy Density: 150–250 Wh/kg (advanced models can exceed 300 Wh/kg)
- Cycle Life: Approximately 1,000–1,500 cycles
- Cost per kWh: Around $100–130
- Thermal Stability: Moderate, with balanced performance
Key Advantages:
- Superior energy density for extended range
- Ideal for long-range electric vehicles
- Mature technology with high market acceptance
Typical Applications:
- Passenger electric vehicles (EVs)
- Residential and commercial energy storage
- Consumer electronics like laptops and drones
What is an LFP Battery? – Balancing Safety and Longevity

The LiFePO4 lithium battery, commonly referred to as LFP, has gained popularity in the renewable energy sector for its excellent safety, extended lifespan, and affordability. While its energy density is slightly lower than NMC, it excels in thermal stability and environmental friendliness. Many LiFePO4 battery manufacturers are now producing reliable options that cater to diverse needs.
- Energy Density: 90–160 Wh/kg (high-end models up to 205 Wh/kg)
- Cycle Life: Over 2,000 cycles
- Cost per kWh: $70–100 (projected to drop to $36–56 by 2025)
- Safety: Virtually no risk of thermal runaway
Key Advantages:
- Exceptional safety and thermal stability
- Long lifespan with low maintenance costs
- Environmentally friendly materials that are abundant
Typical Applications:
- Solar and wind energy storage systems
- Electric buses and commercial vehicles
- Backup power and power tools
What is an LTO Battery? – Champion of Fast Charging and Durability
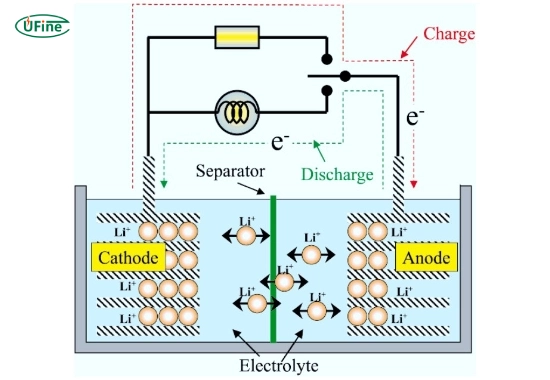
LTO batteries, or lithium titanate batteries, stand out for their ultra-fast charging capabilities and exceptional cycle life, making them perfect for high-end storage and specialized applications.
- Energy Density: 60–120 Wh/kg (the lowest among the three)
- Cycle Life: 5,000–10,000 cycles or more
- Cost per kWh: $150–200
- Charging Speed: Can fully charge in 10–30 minutes
Key Advantages:
- Extremely rapid charging
- Outstanding performance in low and high temperatures
- Ultra-long operational life
Typical Applications:
- Public transportation (electric buses, subways)
- Grid-level energy storage and peak shaving
- Military and aerospace uses
NMC vs. LFP vs. LTO: Key Performance Breakdown
1. Energy Density Comparison
- NMC: Highest, up to 300 Wh/kg – perfect for compact, long-range EVs
- LFP: Moderate, up to 205 Wh/kg – safer but slightly bulkier
- LTO: Lowest, 60–120 Wh/kg – not ideal for high-density requirements
2. Cycle Life Comparison
- NMC: 1,000–1,500 cycles
- LFP: Over 2,000 cycles
- LTO: Leading the pack at 5,000–10,000+ cycles
3. Charging Speed Comparison
- NMC: Medium (1–2 hours)
- LFP: Slower (3–4 hours)
- LTO: Fastest (10–30 minutes)
4. Safety Comparison
- NMC: Some overheating risks
- LFP: Highly safe with strong resistance to thermal runaway
- LTO: Top-tier safety, stable in extreme conditions
5. Cost Comparison
- NMC: $100–130/kWh
- LFP: $70–100/kWh, with potential for further reductions
- LTO: $150–200/kWh – highest cost but justified by longevity
6. Environmental Impact
- NMC: Cobalt mining raises ethical concerns, though recycling is improving
- LFP: Non-toxic and easy to recycle
- LTO: High manufacturing costs, but lower overall carbon footprint due to extended life
Battery Performance Comparison Table
| Feature | NMC Battery | LFP Battery | LTO Battery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 150–250 Wh/kg (up to 300) | 90–160 Wh/kg (up to 205) | 60–120 Wh/kg |
| Cycle Life | 1,000–1,500 cycles | 2,000+ cycles | 5,000–10,000+ cycles |
| Charging Speed | 1–2 hours | 3–4 hours | 10–30 minutes |
| Safety | Moderate | High | Extremely High |
| Cost | $100–130 | $70–100 | $150–200 |
| Typical Uses | EVs, Electronics | Energy Storage, Buses | Grid Storage, Military |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What’s the main difference between NMC and LFP? NMC offers higher energy density for longer-range EVs, while LFP shines in safety, longevity, and lower costs.
- How much do LTO batteries cost? Currently, LTO batteries range from $150–200 per kWh, reflecting their superior lifespan and fast-charging features.
- Which is better for energy storage: LTO or LFP? For cost-effectiveness and long cycles, go with LFP battery; for ultra-fast charging and reliability, LTO is superior.
- Can all three batteries be recycled? Yes. LFP is the easiest to recycle, NMC requires special handling for cobalt, and LTO’s long life reduces recycling needs.
Wrapping It Up: Choosing the Right Battery for You
- Opt for NMC if you need long range and compact size in electric vehicles.
- Choose LFP for a well-rounded option that balances safety, lifespan, and cost – great for storage and commercial vehicles.
- Go with LTO for applications demanding extreme durability and rapid charging, like industrial or public transit systems.
In today’s fast-evolving renewable energy landscape, grasping the strengths and weaknesses of NMC, LFP, and LTO batteries empowers you to strike the perfect balance between performance, affordability, and sustainability for more efficient and secure energy solutions.
